3 Trailblazing Women Who Changed the Fate of Endangered Species!
In the fascinating world of endangered species, the blog explores the urgent and compelling efforts required to protect some of the earth's most vulnerable animals. Highlighting the critical work of conservationists like Dr. Amanda Vincent and Dr. Patricia Wright, the blog delves into their groundbreaking research and tireless advocacy for marine life and lemurs, respectively!
World Endangered Species Day is a moment each year to reflect on the importance of protecting the planet's most vulnerable species. It's also an opportunity to highlight the trailblazing women who have devoted their lives to understanding and conserving these creatures. Their research changed our scientific knowledge about endangered species but also influenced global conservation policies. This blog post explores the contributions of these women and the impact they have had on the animals of this planet.
Unlocking STEM Potential
Download our “Parent’s guide to Confident Girls" today and learn ways to foster confidence and passion for STEM in your little one this year.
The Importance of Protecting Endangered Species
The world is home to a stunning array of biodiversity, yet many of its species are teetering on the brink of extinction. Endangered species from various corners of the globe highlight the urgent need for conservation efforts to ensure their survival.
The importance of protecting endangered species is well-documented in scientific literature. Each species plays a unique role in its ecosystem, and the loss of any can have unforeseen consequences that destabilize entire ecological networks. There are dedicated researchers who work tirelessly to understand and protect our planet's most vulnerable creatures.
Among these researchers, numerous women have made significant contributions, breaking barriers in the predominantly male-dominated fields of STEM and zoology. This blog post highlights some of these remarkable women, their research, and the ongoing importance of protecting endangered species.
Dr. Amanda Vincent & Her Seahorses
In the vast and mysterious world of ocean life, seahorses captivate the imagination with their unique charm and surprising fragility. They have several unique features that distinguish them from other marine life such as the fact that they have no stomachs and their males give birth to their young.
Dr. Amanda Vincent a Canadian marine biologist, has significantly shaped the global approach to the conservation of these remarkable creatures. As the first biologist to study seahorses underwater, Vincent's research has unveiled insights into the behaviour, ecology, and threats facing seahorses. Her studies have highlighted the vulnerability of seahorses to overfishing and habitat loss, particularly from trawling and coral degradation.
One of Dr. Vincent’s most notable impacts is her role in getting seahorses listed under the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES), significantly regulating the international trade of these species. Her research has provided a foundation for policy changes and management practices that aim to ensure sustainable trade levels that do not compromise the species' survival. This approach has been a model for subsequent efforts to protect other marine species impacted by international trade. Through her tireless work, Dr. Vincent has not only safeguarded the future of seahorses but also inspired a new generation of conservationists to protect our world's oceans.
Dr. Patricia Wright & The Golden Bamboo Lemur
The animated film "Madagascar" captivated audiences worldwide with its humorous and endearing portrayal of the charismatic and playful lemurs, led by King Julien. This brought a spotlight to these unique creatures and their exotic homeland. The popularity of the movie increased public interest and awareness of lemurs, a diverse group of primates found only in Madagascar.
In the 1980’s Dr. Patricia Wright went on her first expedition to Madagascar where she discovered a new species of lemur, the golden bamboo lemur, previously unknown to science. This small primate, characterized by its dense golden fur and piercing green eyes, feeds predominantly on the cyanide-laden shoots of the giant bamboo, consuming up to 12 times the lethal dose of cyanide for most other animals each day. Dr. Wright's extensive field studies have revealed fascinating aspects of its diet and behaviour, demonstrating a remarkable example of evolutionary adaptation.
The golden bamboo lemur was a catalyst for the establishment of Ranomafana National Park, a critical sanctuary for this species and many others. Opened in 1991, this park covers more than 41,500 hectares of rainforest and is home to several species of endangered lemurs. Dr. Wright’s efforts in founding and managing the park have been pivotal in providing a sanctuary for these primates, ensuring their protection and the preservation of their natural habitat.
Dr. Jane Goodall & Chimpanzees
Jane Goodall is a name synonymous with chimpanzees and conservation. In 1960, at the age of 26, without formal university training in wildlife biology, Goodall embarked on what would become a lifetime of groundbreaking work, under the mentorship of famed anthropologist and paleontologist Louis Leakey.
Goodall's early observations challenged the prevailing scientific consensus of the time, which held that only humans could construct tools. She discovered that chimpanzees not only make tools but also use them to fish for termites, a behavior that suggested a level of sophistication and intelligence that had not been previously attributed to non-humans. This discovery was profound, blurring the line between humans and animals and suggesting that we share more similarities than previously thought.
Moreover, Goodall's research extended beyond just tool use. She observed complex social behaviors in chimpanzees, including their capacity for emotion, such as joy, sorrow, and even empathy. Jane's method of giving names to her research subjects instead of numbers, a practice unusual at the time, helped her make detailed, longitudinal studies on individual chimpanzees, which continue to inform current research and conservation strategies.
Conclusion
On World Endangered Species Day, it is essential to recognize and celebrate the contributions of women scientists who have made significant impacts in the field of conservation. Their relentless pursuit of knowledge and dedication to protecting the planet’s most vulnerable species continue to inspire and lead future conservation efforts. By supporting and promoting women in science, we not only achieve a more equitable scientific community but also enrich the entire field of conservation with diverse insights and robust solutions.
The Ripple Effect: Unraveling the Impact of Low Self-Efficacy on Young Women
Parents, your support is crucial in shaping your daughter's confidence and belief in her abilities. Our latest blog explores the sociology behind self-efficacy and provides actionable steps to help you boost your daughter's self-efficacy, especially in STEM fields!
Studies show that by the age of 6, young girls have already begun to make decisions about the things they think they can and cannot do. In developing ability in young girls, self-efficacy emerges as a pivotal thread, weaving through aspirations, behaviours, and social interactions. Defined by the renowned psychologist Albert Bandura, self-efficacy refers to an individual’s belief in their capabilities to execute tasks and achieve goals. It is not just about having the skills but also the confidence to use those skills effectively. This nuanced element of personal development is profoundly influential yet often overlooked, particularly among young women. It casts a long shadow, affecting their aspirations and achievements, especially notable in fields like STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) where they are already underrepresented.
Unlocking STEM Potential
Download our “Parent’s guide to Confident Girls” today and learn ways to foster confidence and passion for STEM in your little one this school year.
The Impact of Self-Efficacy on Learning STEM Subjects
When young girls have low self-efficacy in STEM subjects, it affects their willingness to engage with and persist in learning these subjects. They may doubt their abilities, shy away from challenges, and feel less confident in their problem-solving skills. This lack of confidence can lead to a cycle of underperformance, reinforcing their belief that they are not capable in these areas. Consequently, girls may opt out of advanced STEM courses, participate less in class, and show a diminished interest in pursuing STEM careers.
The Sociology Behind Self-Efficacy
Self-efficacy, as conceptualized by Bandura, is a core component of his social cognitive theory, which emphasizes the interplay between personal factors, behavior, and the environment. According to this theory, individuals develop self-efficacy through four main sources: mastery experiences, vicarious experiences, social persuasion, and physiological states.
Sociologically, these sources are deeply embedded in the social context in which individuals operate. For young girls, societal norms, cultural messages, and educational environments significantly influence their self-efficacy beliefs.
Social Persuasion and Stereotype Threats
Social persuasion involves the encouragement or discouragement individuals receive from others. Teachers, parents, and peers significantly impact young girls’ self-efficacy through their feedback and expectations. Positive reinforcement and constructive feedback can enhance self-efficacy, while negative comments and low expectations can undermine it. Physiological states, such as anxiety and stress, also affect self-efficacy. The pressure of stereotype threat can also heighten anxiety and lower self-efficacy among girls studying STEM.
Stereotype threats happen when individuals feel at risk of conforming to negative stereotypes about their social group. For girls in STEM, the pervasive stereotype that boys are naturally better at math and science can lead to increased anxiety and reduced performance. For example, studies show that young girls often underperform when they are aware that the teacher marking their tests will be a man.
In this case, the awareness of this stereotype is enough to negatively impact a young girls academic performance, creating a self-fulfilling prophecy that undermines their confidence and interest in STEM subjects.
Overcoming the Gap of Self-Efficacy
To combat the negative impacts of low self-efficacy, it is essential to create supportive learning environments that challenge stereotypes and foster a growth mindset. A growth mindset, a concept developed by psychologist Carol Dweck, emphasizes the belief that abilities and intelligence can be developed through dedication and hard work. This contrasts with a fixed mindset, where individuals believe their qualities are static and unchangeable. By promoting a growth mindset, we can encourage young girls to embrace challenges, persist in the face of setbacks, and see effort as a path to mastery.
Encouraging girls to take risks, make mistakes, and view challenges as opportunities for growth is crucial in building self-efficacy. In many educational settings, the fear of failure can be particularly paralyzing for girls, who may feel additional pressure to meet perfectionist standards or avoid confirming negative stereotypes about their gender. Creating an environment where mistakes are viewed as a natural part of the learning process and where perseverance is celebrated can help girls develop resilience and a stronger belief in their capabilities.
Role models and mentors in STEM fields play a vital role in this process. Seeing successful women in STEM provides tangible examples of what is possible and helps to counteract the stereotype that STEM is predominantly a male domain.
Conclusion
The sociology behind self-efficacy reveals the profound impact of societal influences on young girls' engagement with STEM content. By understanding and addressing these sociological factors, we can create a more equitable and empowering educational landscape. Ensuring that young girls develop strong self-efficacy beliefs is not just about boosting their confidence—it is about unlocking their potential to contribute meaningfully to the world of STEM. As we strive to break down barriers and challenge stereotypes, we pave the way for a future where girls can confidently pursue their passions and excel in STEM fields.
Building Dreams in the Sky: The Women Behind Some of the World's Most Stunning Skyscrapers
The science of skyscrapers is a fascinating blend of engineering, architecture, and materials science, creating structures that defy gravity and define skylines. Women like Jeanne Gang and Zaha Hadid have shown that gender is no barrier to success in this field, inspiring young girls to pursue their dreams in STEM. By fostering creativity and providing support and opportunities, we can encourage the next generation of female architects and engineers to reach for the sky, building the skyscrapers of tomorrow.
Skyscrapers are some of the most impressive buildings of modern engineering and they stand tall as symbols of human ingenuity and creativity. These tall structures, sometimes piercing the clouds, are a testament to the impact of science and technology. Building a skyscraper involves a blend of architecture, engineering, and materials science, all working together to create something that is not only tall but also safe, functional, and aesthetically pleasing.
Unlocking STEM Potential
Download our “Parents Guide to Confident Girls" today and learn ways to foster confidence and passion for STEM in your little one this school year.
The journey of building a skyscraper begins deep below the surface. The foundation is the most critical part of any tall structure, providing the stability needed to support the immense weight. Engineers conduct soil tests to determine the best type of foundation.
The science behind these decisions ensures that the skyscrapers remains stable and secure, even under the stress of their own weight, wind, and seismic activity. By highlighting the science behind skyscrapers and the contributions of women in this field, we can inspire a new generation to dream big and pursue STEM careers with confidence and creativity.
Jeanne Gang: Redefining Architecture
Jeanne Gang established Studio Gang Architects in 1997, and since then, she has pushed the boundaries of architectural design. Her philosophy revolves around creating buildings that respond to their environments and enhance the space’s natural surroundings. She believes in architecture's power to address pressing social issues and improve the quality of life for people.
One of Jeanne Gang’s most celebrated projects is the Aqua Tower in Chicago. Completed in 2010, this 82-story mixed-use skyscraper is a striking addition to the city’s skyline. The Aqua Tower is notable for its undulating, wave-like facade, which is both an aesthetic triumph and a functional innovation.
The facade's design was inspired by the natural forms of limestone outcroppings commonly found in the Great Lakes region. This unique exterior creates a dynamic visual effect, as the building appears to change shape when viewed from different angles. The design also serves practical purposes: the undulating balconies help to break up wind currents, reducing the building’s sway and providing wind protection to the residents.
Zaha Hadid: The Architect of the Future
Zaha Hadid, often hailed as the "Queen of the Curve," redefined the boundaries of architecture with her innovative and futuristic designs. As the first woman to receive the Pritzker Architecture Prize, Hadid's work is characterized by fluid forms and dynamic spaces that challenge conventional architectural norms. Her buildings are not just structures but expressions of movement and transformation, pushing the limits of engineering and design.
Fluid forms are characterized by their seamless and continuous surfaces, which create a sense of movement and flow. These forms are not only visually striking but also functionally efficient, allowing for optimized circulation and for more organization of the building . Dynamic spaces are designed to be flexible and adaptable, capable of transforming to meet different needs and uses.
The Heydar Aliyev Center exemplifies Zaha Hadid’s mastery of fluid forms. Its undulating design challenges conventional architectural norms and showcases the potential of advanced computational design and engineering. The building is a testament to Hadid’s visionary approach, pushing the boundaries of architecture and inspiring a new generation of architects to explore bold and innovative designs. The Heydar Aliyev Center not only serves as a cultural landmark but also as a symbol of the transformative power of architecture.
The Relationship Between Creativity and Architecture
Architecture is inherently a creative discipline, and creativity is essential for pushing the boundaries of what is possible. Research in the Creativity Research Journal emphasizes that architectural creativity is not just about aesthetics but also about functional innovation.
Creative architects can envision spaces that are both beautiful and practical, addressing human needs in novel ways. This creativity is nurtured through a combination of education, experience, and a willingness to take risks and think outside the box.
It is a wonderful blend of how STEM can be experienced in different ways and it is a great avenue to get your little girl interested in a branch of science that is so multi-faceted.
Conclusion
The science of skyscrapers is a fascinating blend of engineering, architecture, and materials science, creating structures that defy gravity and define skylines. Women like Jeanne Gang and Zaha Hadid have shown that gender is no barrier to success in this field, inspiring young girls to pursue their dreams in STEM. By fostering creativity and providing support and opportunities, we can encourage the next generation of female architects and engineers to reach for the sky, building the skyscrapers of tomorrow.
Celebrating Mothers: Champions of Daughters in STEM
This Mother's Day, let's celebrate and recognize the incredible impact mothers have on their daughters' journeys into the realms of Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics (STEM). Our latest blog post delves into the pivotal role that moms play in shaping their daughters' attitudes toward these critical fields.
As we approach Mother's Day, it's a wonderful opportunity to reflect on the pivotal role mothers play not only in the nurturing and overall development of their children but also in shaping their educational and career aspirations. Mothers are often the first teachers and role models for their daughters, providing them with the encouragement and support needed to pursue their dreams. This influence is especially critical in the fields of Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics (STEM), where women have historically been underrepresented. In this blog, we'll explore how mothers are crucial in encouraging their daughters to pursue STEM education, highlighting research that underscores the importance of parental buy-in and the special role of maternal support in boosting confidence and interest in science and technology.
Unlocking STEM Potential
Download our “Parent’s guide to Confident Girls” today and learn ways to foster confidence and passion for STEM in your little one this school year.
Mom’s Are The Foundation of Support
The profound influence of mothers on both the emotional and intellectual growth of their children is well-documented and particularly impactful during the formative years of early childhood. This developmental phase is critical as it sets the groundwork for lifelong attitudes toward learning and education.
According to a study published in the Journal of Research in Science Teaching, mothers who hold and express positive views about STEM—particularly science and math—tend to instill similar sentiments in their daughters. This influence extends beyond mere exposure to the subjects; it cultivates an environment where girls feel capable and motivated to engage with challenging content.
This maternal encouragement is not only about promoting interest but also about shaping self-perception in STEM capabilities. A positive maternal influence helps counteract common stereotypes that might otherwise deter girls from pursuing STEM disciplines. It fosters a self-image of competence and suitability for these fields at a young age, which is crucial for sustaining interest and engagement as educational opportunities in STEM arise later in school.
Mom’s Encourage Risk Taking
Mothers play a crucial role not only in shaping positive attitudes towards these subjects but also in influencing their daughters' willingness to take risks.
An essential aspect of risk-taking involves dealing with failure. Mothers who create a supportive environment where failure is seen as a learning opportunity rather than a setback instill resilience in their daughters. By emphasizing the value of persistence and learning from mistakes, mothers help their daughters develop the confidence needed to take risks. This approach is particularly important in STEM, where experimental failures can often lead to greater understanding and breakthroughs.
Finally, the expectations mothers set for their daughters can influence their willingness to take risks. Mothers who expect their daughters to perform well, challenge themselves, and not shy away from difficult paths send a powerful message about the value of ambition and courage. These expectations, coupled with the support and resources to achieve them, encourage daughters to take the necessary risks that come with pursuing careers in STEM.
Mom’s Are Confidence Builders
Confidence is a cornerstone of success in any challenging field, particularly in STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics), where the problems faced can be complex and demanding. The importance of confidence is underscored by the findings that women, more often than men, tend to underestimate their abilities in STEM-related areas. This disparity can lead to fewer women entering or persisting in these fields, potentially missing out on fulfilling careers and the opportunity to contribute to significant scientific and technological advancements.
The impact of self-doubt is not trivial; it influences career choices, academic engagement, and persistence in STEM disciplines. However, mothers play a pivotal role in mitigating these doubts and fostering a robust sense of capability in their daughters. Research published in Developmental Psychology by Eccles in 1994 illuminates this dynamic effectively.
According to the study, girls who receive strong and affirming support from their mothers develop a more positive self-concept in mathematics, which is often considered one of the foundational pillars of STEM education. This positive self-concept extends beyond just feeling good about one’s abilities—it influences the likelihood of engaging with difficult material, participating in STEM-related activities, and choosing to pursue further studies and careers in these fields.
Conclusion
We already know mothers are magical and have superhuman strength but mom’s who actively encourage their daughters, celebrate their efforts (regardless of outcomes), and affirm their ability to solve problems help cultivate a mindset in which challenges are seen as opportunities to learn and grow rather than insurmountable obstacles. This kind of support helps young women internalize the belief that they are competent and capable of succeeding in anything they do. So to all the wonderful moms out there, we appreciate you, we love you, and we will never forget all you’ve done for us.
The Interplay of Humor and STEM Education: Celebrating the International Day of Laughter
Discover the surprising connection between humor and STEM education in our latest blog post, "The Interplay of Humor and STEM Education: Celebrating the International Day of Laughter." Delve into how laughter not only lightens the mood but significantly enhances learning outcomes in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics. From boosting memory retention to fostering creative problem-solving, find out why incorporating humor into STEM subjects could revolutionize the way these disciplines are taught.
May 5th marks the International Day of Laughter, a perfect occasion to explore the often-overlooked connection between humor and education, particularly within the disciplines of Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics (STEM). While STEM subjects are traditionally viewed as serious and rigorous, incorporating humor into their teaching can not only lighten the mood but also enhance learning outcomes, foster creativity, and promote a deeper engagement with the material.
Unlocking STEM Potential
Download our “Parent’s guide to confident Girls" today and learn ways to foster confidence and passion for STEM in your little one this school year.
The Benefits of Laughter in Learning
Laughter, a universal language of joy, has numerous psychological and physiological benefits. It reduces stress hormones such as cortisol and adrenaline, boosts the immune system, and increases the intake of oxygen-rich air, thereby stimulating the heart, lungs, and muscles. From a psychological standpoint, laughter releases endorphins, promoting an overall sense of well-being and temporarily relieving pain. In the context of education, these benefits can translate to increased attention, better memory retention, and a more positive learning environment.
Humor's Role in STEM Education
The infusion of humor into STEM education can break down the intimidating barriers that these subjects often erect. Research suggests that humor can help students process and remember information, as the enjoyment it sparks increases attention and improves retention. For instance, Banas et al. (2011) explored how humor enhances the learning process by making it more engaging and less threatening, which is particularly beneficial in challenging subjects like mathematics and science.
Moreover, humor encourages divergent thinking—a vital component of creativity and problem-solving in STEM fields. A study by Ziv (1983) demonstrated that humor enhances the ability to solve problems by increasing the flexibility of thinking and broadening the associative processes in the brain. This is crucial in STEM education, where innovative solutions and approaches are highly valued.
Real-World Applications and Anecdotes
Incorporating humor into STEM can take various forms, from humorous examples in mathematical problems to funny anecdotes that relate to scientific concepts. For instance, a chemistry teacher might use a pun about molecules—"I told a chemistry joke once, but there was no reaction"—to lighten the mood and make the subject matter more accessible. Such strategies not only make learning enjoyable but also help students to visualize complex concepts in a relatable way.
Educators who employ humor report a more dynamic interaction with their students and observe higher levels of engagement and curiosity. This anecdotal evidence is supported by educational theories that posit learning as a holistic, emotional experience, where students’ engagement is as crucial as the information being imparted.
Challenges and Considerations
While the benefits of using humor in education are clear, it comes with challenges. The key is to ensure that the humor is appropriate, inclusive, and aligns with educational goals. Teachers must be mindful of cultural sensitivities and personal boundaries to ensure that their use of humor fosters a positive and inclusive classroom environment.
Conclusion
On the International Day of Laughter, it is essential to recognize and promote the use of humor as a powerful educational tool, especially in the fields of STEM. By integrating laughter and fun into these subjects, educators can create a more engaging, enjoyable, and effective learning environment. As research continues to unfold the layers of benefits provided by humor, it becomes increasingly clear that laughter might just be one of the most serious tools in the educational arsenal.
The History of Witch Hats and Alewives: A Toast to Women in STEM
Each Halloween, streets are flooded with an array of mystical creatures, superheroes, and iconic figures. Amidst the sea of costumes, one particular image stands out — the witch with her tall, pointy hat. But the story behind this iconic hat, and its intriguing connection to alewives, dives deep into the history of early women in STEM and the science behind brewing. Join us on this journey as we uncover the magical blend of history, science, and societal evolution.
Halloween is a fun holiday bursting with rich histories. Among the colourful costumes, one that stands out time and time again is the witch, complete with her pointy hat. But have you ever wondered how this iconic symbol became associated with witches? Let's unravel this story, which surprisingly connects into the world of science and the early women in STEM.
This Halloween pick a costume filled with confidence!
Download our “Parent’s guide to Confident Girls” today and learn ways to foster confidence and passion for STEM in your little one this school year.
Witches and Their Pointy Hats
Historically, women who defied societal norms or exhibited unexplainable behaviors were often vilified and, in many cases, branded as witches. The pointed hat, or the "witch's hat," has blurry origins, but its association with these marginalized women is a testament to how society marks and remembers those who don't fit within the times. Some theories suggest that the pointy hat was a symbol of fear and mistrust, and in medieval Europe, such hats were forced upon people who were considered different or heretics so they could be easily identified. Over time, this hat became synonymous with witches, especially during the witch trials and hunts.
Alewives and The Art of Brewing
From the early 14th century to the late 18th century, the most popular drink was ale, also known as small beer. Long before commercial breweries took over, brewing beer was primarily a household chore, often falling under the duties of women. These women, known as alewives, were masters of fermentation, and their skills were often sought after. They would craft their brews in large cauldrons, stirring with long wooden paddles and selling in the local markets.
The alewives had distinct ways to signify that their brew was up for sale. They'd hang a broomstick or "ale-stake" outside their door or above their taverns. Over time, rumors started and these broomsticks became associated with witches flying in the night, and the bubbling cauldron of brew became the potion pot of a witch.
The Science Behind Brewing
Alewives were essentially early chemists. The brewing process, while seemingly straightforward, requires a precise balance of ingredients and conditions to produce the perfect ale. It begins with the malting process, where grains, typically barley, are soaked in water and allowed to germinate. This process converts stored starches into sugars, essential for fermentation.
Next, the grains are roasted to develop flavor and color. The degree of roasting can vary, leading to different types of beers from pale ales to stouts. The roasted malt is then mashed with hot water in a process called mashing, extracting fermentable sugars. The resultant liquid, known as wort, is boiled and hops are added for bitterness, flavor, and aroma.
Finally, yeast is introduced to the cooled wort, and fermentation begins. Yeast, a microorganism, consumes the sugars in the wort and produces alcohol and carbon dioxide in the process. This biochemical reaction was harnessed and perfected by alewives long before it was understood scientifically.
Women in STEM: A Legacy from Brewing to Modern Day
The alewives, with their innate understanding of the brewing process, can be seen as early women in STEM. Their experimental nature, dedication, and the scientific approach to brewing laid the foundation for many women who followed, breaking barriers in fields once dominated by men.
Today, as we celebrate women in STEM, we recognize their invaluable contributions across all domains of science and technology. From brewing to biotechnology, women have played and continue to play a pivotal role in shaping our understanding of the world.
A Toast to Women in STEM
So, this Halloween, as you spot the occasional witch with her pointy hat, remember the alewives. Raise a toast to the pioneering spirit of these women, the original women in STEM, who blended craft with science, leaving an indelible mark on history.
Empowering Young Girls in STEM: A Back to School Guide
As the new school year begins, a pressing challenge remains: bolstering confidence in young girls for STEM fields. From shining a spotlight on STEM heroines like Ada Lovelace and Dr. Mae Jemison to encouraging hands-on experiments and questioning, it's crucial to nurture their natural curiosity. By dispelling gender stereotypes and emphasizing real-world STEM applications, we pave the way for our girls to see themselves as tomorrow's innovators. With a blend of mentorship, resources, and community support, we can assure every young girl that she belongs in the ever-evolving world of Science, Technology, Engineering, and Math
As the school bells ring and students shuffle back into the classrooms, there's one area that often needs a little extra attention for young girls: confidence in STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Math). With a world increasingly reliant on technology and innovation, ensuring our young ladies feel empowered and capable in these critical areas is more important than ever. Let's explore how we can foster their passion and self-assuredness in STEM.
Unlocking STEM Potential
Download our “Parent’s guide to Confident Girls" today and learn ways to foster confidence and passion for STEM in your little one this school year.
1. Representation Matters
Shine a Light on STEM Heroines. Introduce your girl to prominent women in STEM, from historical figures like Ada Lovelace and Rosalind Franklin to modern icons like Dr. Mae Jemison and Reshma Saujani. Knowing that women have paved the way can inspire her to follow in their footsteps. Watch out for our “Role Model of the Week” posts to learn more about women in STEM who were pioneers of their generation.
2. Hands-On Learning
Engage Curiosity Through Doing. Whether it's at-home science experiments, coding projects, or building tasks, hands-on activities help solidify understanding and can spark a passion for STEM subjects. An awesome example is seeing who can build the tallest towers with the cardboard center of paper towels and some newspaper. It’s a fun activity and there are so many things to discuss like what attributes make a strong structure or the best shape for the base of a tall building.
3. STEM Clubs and Groups
Foster Community. Many schools offer STEM clubs or groups that focus on robotics, coding, science, and more. Being surrounded by peers with similar interests can nurture her passion and confidence. If there are no clubs in your daughter’s school, consider starting a Lego robotics club! FIRST is an incredible program that lets kids experience STEM through the excitement of Lego and robot competitions!
4. Focus on Real-World Applications
Why Does STEM Matter? Studies show that young girls tend to choose careers that will have a positive impact on society. Many STEM topics are focused on the technical aspects of the subject matter but there are endless opportunities to create new things that can make huge changes in the world. Show her the real-world applications of what she's learning. Visit museums, go on nature hikes, or attend tech fairs. When she sees STEM in action, she can visualize her place in it.
5. Celebrate Failures as Learning Moments
Redefine Success. It's essential to teach resilience in the face of challenges and encourage self-efficacy. Self-efficacy is a social concept that describes a person’s belief in their own ability to do what is necessary to reach their goals. It means giving your little girl the space to fail and understand that it is natural for things to go wrong but there is always space to improve Highlight that every failure is a step closer to understanding and success. Encourage a growth mindset.
Conclusion
Building confidence in young girls for STEM subjects isn't just about academic achievements. It's about nurturing curiosity, challenging norms, and providing ample opportunities for exploration. As the school year unfolds, let's make a collective effort to ensure every young girl knows she has a place in the world of STEM
Top 3 Halloween STEM Activities This Season
It’s Valentine’s Day weekend, and Love is definitely in the air! But that doesn’t mean science can’t be as well!
What would you say if I told you there was an invisible force in the air drawing you closer to the center of the earth? Sounds spooky, but we’re just talking about gravity. It’s science! Science has answers to natural phenomena that when observed, could send a chill down your spine. What better way to explore STEM this Halloween than engaging in some fun experiments?
Below are some of The Top 3 of Halloween experiments you can do this year with household items and candy. It wouldn’t be Halloween without the candy!
Milky Madness
Materials:
3.5 % Milk
A glass bowl
Dish Soap
Q-Tip or Pipette
Food colouring (MUST contain propylene glycol)
Instructions
Pour a cup of the 3.5% milk into the glass bowl.
Carefully create a spooky pattern using your food colouring.
Add a drop of dish soap.
Watch as the milk spreads and comes to life.
Repeat with different patterns.
Explore
Have you ever noticed how much easier it is to move in a pool when you’re fully underwater versus when you are halfway in? That’s because water has very high surface tension. Surface tension is a property of liquids where their particles are attracted to one another at the surface.
In this experiment, we manipulated surface tension using milk, food dye and dish soap. We said earlier that water has very high surface tension but so does milk. When the dye is dropped into the milk, the drops are held together because of the milk’s high surface tension.
Dish soap on the other hand is a surfactant and these types of liquids reduce surface tension! Once the dish soap is added to the mixture, the fat particles in the milk move freely, making the dye swirl around.
Marshmallow Ghouls
Ever been camping, telling ghost stories over the fire, and you notice your marshmallow swelling until it falls off the stick?! Well in this experiment, we will investigate what happens to marshmallows when they get hot.
Materials:
Jumbo marshmallows
Paper plate
Food dye
Paintbrush
Food-safe markers (optional)
Instructions:
Get your marshmallow and measure the height.
Decorate your scariest ghosts and goblins on your marshmallow.
Set the marshmallows on the paper plate.
Place in the microwave for 15-30 seconds. (This may vary dependent on the microwave)
Watch as the marshmallows expand.
Measure the height of your marshmallow after.
Make observations on how the marshmallow changed in size what happened to the patterns after they were heated.
Explore
Believe it or not, marshmallows are made of sugar, water and a whole lot of air bubbles. When a marshmallow gets heated up, the water molecules vibrate and get hot. The heated water warms up the sugar as it gets softer.
The sugar warms the air bubbles which move faster inside the marshmallow. As the air bubbles bounce around, they push on the walls of the bubble which expand and make the marshmallows puff up!
Candy Corn Gone Wrong
Have you ever found yourself eating a piece of candy and wishing it wouldn't dissolve so fast in your mouth? Well, this experiment will be exploring how long it takes for candy corn to dissolve in different solution.
Materials
Candy corn
Baking soda
Salt
Vinegar
Water
4 transparent cups
Recording sheets
Instructions
Label the cups: Water, Water & Salt, Water & Vinegar, Water & Baking Soda
Fill the first cup with 1 cup of water.
Fill the second cup with 1 cup of water and ½ a tablespoon of salt and stir.
Fill the fourth cup with 1 cup of water and 2 tablespoons of vinegar.
Fill the third cup with 1 cup of water and a tablespoon of baking soda and stir.
Place a candy corn in each cup.
Eat some chocolate while the candy corns dissolve.
Write down what you see in the observation sheet. Which solution dissolved the candy fastest?
Explore
In this experiment, we are exploring what happens when different liquids a solid are mixed together to form a solution. The solid in this case is the candy corn and the liquids are made up water and other substances. We are seeing the candy corn dissolve in the different liquids because the particles interact. We are looking to see which cup will dissolve the candy corn quickest. There are a few things that will make a solid dissolve faster in a particular liquid as seen below:
When the liquid and solid are stirred.
When the liquid is warmer.
When the solid is made up of smaller particles with more surface area.
When we did our experiment, we will noticed that the candy corn dissolved fastest in the water that had salt included. Did you notice something different?
Have a happy Haloween!!
Top 3 Valentine's Day STEM Activities
It’s Valentine’s Day weekend, and Love is definitely in the air! But that doesn’t mean science can’t be as well!
It’s Valentine’s Day weekend, and Love is definitely in the air! But that doesn’t mean science can’t be as well! If you’re looking for something fun to do this weekend, check out the Top 3 Valentines Activities that involve science! They’re easy, cheap and a whole lot of fun!
You will need a few things for this experiment and you can get most of them at the local Dollar Store. Here is a list of everything I used for these Valentine’s Day Projects:
Materials:
Plastic Hearts
A Vase/Bottle
Red Food Colouring
1 L of Oil
1 Cup of Water
Alka-Seltzer
Paper
White Crayons
Red Paint /Purple
Cooking Chocolate
Plastic Hearts Mold
Let The Fun Begin!
Love Lava Lamp
Lava lamps are those fun lamps that you sometimes see in specialty stores or sitting on the living room of your eccentric auntie. And guess what?! You can make your own lava lamp at home and the process is much cooler when you do it yourself.
The idea behind home made lava lamps are a great way of observing how science contributes to our day to day lives. In this activity, you see both a chemical reaction and the consequences of polarity in molecules. Making the lava lamp is easy and a delight to watch!
To make the lava lamp you will need:
Food Dye,
Alka Zelter,
500mL- 1L oil,
1 cup of water.
Vase/2L bottle
Plastic Hearts
Steps:
Pour the cup of water into your vase. I used a vase because it was what I had available but you can easily use a 2L bottle
Next, pour all the oil in slowly to avoid the two liquids from mixing. You may need to wait a few minutes for the liquids to be completely separated.
3. Once separated you can add the food dye. You can use as many colours as you like! You can add any plastic hearts or sequins at the same time. (I used foam and plastic in mine)
4. Drop an Alka Seltzer tablet in the vase and watch your Lava Lamp come to life! I had to make a video because it was so much fun!
Why don't the water and the oil mix?
During the activity, the oil floats on the water like a fish in the sea! Why is that? It all has to do with electric charges! Water molecules carry a positive charge at one end and a negative at the other. The charges are attracted to each other and join to make hydrogen bonds. However, oil molecules carry no charge. These fundamental differences are enough to make the two liquids enemies of sorts. The oil molecules will stick together and so will the water molecules so they will not mix.
Questions: How do you wash away an oil spill if it won’t mix with water? Why is the oil on top and not the water?
Bubbly reaction?
My favourite part of this activity are the bubbles! The reaction is fun to watch as the water fizzles and the colours can be brilliant! So what’s happening here really? It all has to do with the ingredients of the Alka-Seltzer tablet: citric acid and sodium bicarbonate(baking soda). When the tablet hits the water, the two compounds react and create the fizzy show that you see! You can create the same effect with baking soda and vinegar
Questions:Why do some substances react and others don’t?
Invisible Messages
The next activity ties in perfectly as it draws on some of the concepts we talked about for the Lava Lamp. This one was one of my favourite art projects in school and you can have a lot of fun with it! To create an invisible message you will need:
White Crayola Crayons
1 Cup Water
Red paint
Paper
Wooden Stencils (optional)
Paint Brush
Steps:
1. Write your secret valentines message on the paper with white crayons.
2. Pour 1 cup of water into a bowl and mix with a dollop of paint. Stir until watery.
3. Brush lightly over the message and watch as the message appears underneath the paint
Why does the message show up on top of the paint? **Hint:What doesn’t mix well with water?**
If you guessed that the crayons are made with oil, then you would be right! Crayons are often made with parafin wax which comes from petroleum oil. From the first activity, we know that water and oil molecules don't mix well!
Change of Hearts
Last but not the least, we can explore changes of states by making chocolate hearts! Yumm! Here is a list of what you will need for this delicious activity:
Chocolates
A bowl/ Paint Pallet
Plastic hearts mold
Food dye
Steps:
Bring out the chocolate from the box. **Note that it is in it’s solid state at that point*
Melt the chocolate at very low heat or place in the microwave in 1 minute intervals until it is in liquid form.
3. Once the chocolate is melted, pour into the plastic mold.
4. Decorate any chocolates as you like.
5. Place in the freezer for an hour
6. Once the chocolates have set, go ahead and eat the delicious treats!
What changed in the chocolate?
The chocolate started off as big rectangle sugary blocks and we were able to change the shape and create Valentine’s Hearts! It’s all related to states of matter. Matter is anything that occupies space and has mass. There are three states of matter in the physical world and they are solids, liquids and gases.
The molecules in a solid are closely packed together, however they are constantly vibrating even though we may not see it. Solids hold their own shape like the chocolate before it melted.
When the chocolate was heated, the molecules began moving faster because of the increase in temperature. This caused the chocolate to become a liquid. The molecules in a liquid can move and slide past one another, making them free flowing. Liquids can also take the shape of whatever container they are in which is the reason we poured them into heart shaped molds! Once the chocolate was placed in the freezer, it returned to its solid state.
There were no visible gases in this experiment, however a gas has plenty of free space in between it's molecules. Gases flow very easily while assuming the volume and shape of their container.
Hope you had a lovely Valentine's Day and ate lots of chocolates!!
What is STEM Learning in 2019?
Sometimes referred to as STEAM, it is the study of Science, Technology, Engineering, (Art), & Mathematics.
WHAT IS STEM?! What is STEM in 2019 and why does it matter?
Well I'll tell you what, it's not the Silent Team of Eating Monsters that’s for sure!
Yes, I have jokes.
What does STEM stand for really?
Sometimes referred to as STEAM, it is the study of Science, Technology, Engineering, (Art), & Mathematics. The STEM fields are often responsible for the innovation and technology that are vital to a countries economic prosperity. In Canada alone, the CANCode program spent $50 million in two years in order to encourage youth K-12 in coding programs. Computer science is just one of the many programs that STEM encompasses and although the definitions of these subjects have changed over time, they remain significant to us as a society.
Most of us have basic understandings of these subjects but what do they really do? And how do these fields affect us as a people?
Science:
The sciences are a systematic way of understanding the physical world through observation. Scientists will watch phenomenon and then test their ideas until they have some conclusion or another. It is the idea of watching something happen and looking for patterns. An environmental scientist might watch the weather and look for patterns that may be unusual. Finding such trends may gives us the opportunity to better predict climate.
For example, I was fortunate enough to work as a research assistant at Dalhousie University in Truro, NS. My job was collecting data on algae blooms that were growing in water reservoirs. Due to the increase in temperature year round, algae blooms are now surviving into the winter months which poses a threat to our fresh water. The scientific aspect of this job was testing the water for chemicals, clarity, oxygen levels and many other causes of the mossy plant. The collection of this information will allow the research team to make predictions for the future and perhaps prevent the loss of our fresh water.
At the reservoir looking for algae blooms!
Technology:
Technologists focus on design thinking while creating a more comfortable human experience by addressing needs and meeting them through innovation. Technologists work closely with or are often scientists themselves because their work involves identification of an issue through observation.
Creativity is an integral part of the design process as it often involves coming up with out of the box solutions to problems that have never been tackled before. The use of computers make it much easier for technologists to test and validate new ideas and concepts. When I worked as a research assistant, we used a GPS technology to navigate through the reservoir. The GPS had the saved locations of different spots on the reservoir. and using the device allowed us to test the same area every time we went to the water. This safeguarded the data we collected and made sure our numbers did not change because of things like water depth.
Engineering:
Engineering is the application of science and technology used to solve real world problems. Engineers come together to design and build machines and structures that can be later used by specialists or society in general.
Engineers use problem solving concepts to tackle complex issues that require them to design, test and validate solutions. A great example of engineering is the centrifuge! While working on the algae research, it was necessary to separate the algae from the water and we had to use a machine called a centrifuge.
A centrifuge works a bit like your clothes dryer at home. When the clothes are spinning, they experience centripetal force which tends to pull things inward. While the clothes are spinning the water in them does not experience the force and follows a straight path towards the drum holes. And that's how clothes dry! I'm sure this cat would calm down if it knew about centripetal forces!
Using a similar concept, a centrifuge is engineered so that it can separate mixtures of different densities like algae in water!
Fun FACT: The first centrifuge was used to separate cream from milk!
Mathematics:
Math is the glue that holds Science, Tech, and Engineering together. Maths is used as a way to accurately identify patterns in large amounts of data. Problems are also made easier with mathematics as it allows you to make predictions using past information.
Using mathematics, an engineer can design a bridge strong enough to withstand high winds by calculating how much force the bridge will take. By anticipating these factors with maths, engineers and scientists are able to create safe and useful designs. During my work, all the information I collected was in the form of a numerical value.
So when we take a closer look at the STEM fields, we can see it's really just creative design using mathematics! When I first began my engineering degree, I had an image in my mind of what I would be doing but boy was I wrong! STEM gives individuals the ability to learn how to learn! I do not think every one needs to be a scientist or an engineer, however it is a great skill to be able to always think outside the box and test your ideas!
Meet Hannah Blanchard: The Marine Biologist Who Plays With Giant Squid!
I think I always loved the ocean. I spent several summers sailing with my best friend’s family in coastal Maine growing up, and being on the ocean always kind of felt like home to me.
1. What is Marine Biology and how did you come to love the ocean?
Marine biology is all about studying life in the oceans. Whether it’s microscopic phytoplankton or a blue whale (the largest known animal in Earth’s history), understanding their biology, life histories, behaviour, and potential threats are essential to protecting marine life. The ocean is the biggest ecosystem on Earth, it actually contains about 99% of the total living space, even though it only covers about 70% of the surface. Almost 2000 new marine species are discovered every year; that averages out to around 5 every day!
I think I always loved the ocean. I spent several summers sailing with my best friend’s family in coastal Maine growing up, and being on the ocean always kind of felt like home to me. Pursuing marine biology was a subconscious choice when I was applying to university. It just seemed like the natural thing to do!
2.What animals are your favourite?
There are so many! Sea otters are definitely one, they are just so cute and cuddly looking, and their recovery in the Pacific Northwest is really encouraging!
I also think cuttlefish are pretty much the coolest thing ever, they’re very intelligent and they can literally camouflage themselves into a checkerboard! Sunfish are also amazing, they’re the world’s largest bony fish and they honestly don’t even look real.
3. How do humans interact with the ocean?
No matter where you live on the globe, you’re constantly interacting with the ocean. Every other breath you take contains oxygen produced by marine phytoplankton! Humans rely on the oceans for almost everything, including seafood, oil, gas, shipping, recreation and tourism!
We even need it as a water supply now that desalination plants are essential to providing drinking water in many regions. It’s safe to say any of our behaviours that affect the environment, like producing pollution or greenhouse gases, are going to affect the ocean eventually.
4. What should we be most concerned about with our marine environment?
c Therefore, it’s really essential that we start taking drastic steps to tackle all these issues because we are running out of time to conserve the ocean as we know it.
I think 2018 is going to be a scary year for the oceans. 2017 was the hottest year on record in terms of average global water temperatures. Global CO2 levels have reached an all time high in 2018, which will lead to further climate change and ocean acidification.
Micro-plastics have also been emerging as a huge threat to marine life; they’re present everywhere in the oceans, even the bottom of the Marianas Trench! Overfishing and marine pollution are also major issues in most areas.
On a brighter note, ocean awareness has never been more prevalent, especially on social media. So I think we will start seeing some changes in how people live their lives, and hopefully that leads to changes in environmental law and more widespread conservation efforts!
5. What was the most fun part about working on off shore commercial fishing vessels?
I worked on commercial fishing vessels off Vancouver Island, so I got to seem some amazing remote areas that you can only access by boat. I also got to see a lot of cool marine life.I got to see several different whale species, killer whales, sharks... also some creepy looking deep sea creatures like sea lions, otters, a 2 m long squid, giant Pacific octopus... there are so many!
But it was a really hard job; the hours were long and being out at sea for days at a time without being able to talk to friends and family was challenging. It definitely made me a stronger and more independent person. I really recommend going out of your comfort zone and taking any wild opportunity you can, no matter what sector you work in!
6. What marine wildlife should we be most concerned about?
It’s so hard to pick just one... the north Atlantic right whale is one animal that’s been in the Canadian news a lot the last few years. I think there were at least 17 that died last year out of a population of only 400-500, so it’s a huge issue. Corals are the most at-risk of any marine animal from a climate change perspective, and they’re also really sensitive to overfishing and marine pollution.
7.What was your biggest challenge when studying marine biology?
I think my biggest challenge was trying to decide what area I wanted to specialize in. The field is very broad and I find it all really interesting, so it was hard to stay focused on one area while completing my major term projects. It also can be a depressing field to learn about what is happening in the ocean, but staying optimistic is key to being successful!
8.What can we do to help keep our ocean safe?
As I mentioned before, everything is connected. Any environmentally conscious behaviour is going to make a difference, both on land and in the ocean. Try to produce less waste, take public transportation, only eat certified sustainable seafood, and encourage your friends and family to do the same!
Depending on where you’re located, there are lots of great volunteer opportunities to help clean up and preserve your local environment. You can also participate in movements like signing petitions that advocate for banning plastic straws, offshore drilling, etc. All these little things you can change in your day-to-day life really do add up!
MUST READ: Top 4 Reasons Why Women Should Be In STEM
The wake of the 21st century has seen more development in technology than we are willing to admit. Here are some of the newest innovations coming out of the STEM world
The wake of the 21st century has seen more development in technology than we are willing to admit. Here are some of the newest innovations coming out of the STEM world, just to name a few:
TESLA’s electric, self-driving car.
Hover Boards
Facebook
Netflix
The Apple Watch
Doc from Back to The Future would probably agree that we are well into our flying cars stage. With all these advances, it is important to note that none of those inventions were made by women and there is where the problem lies.
A study found that women account for only 8% of all patent holders and even less in places like Germany (3.2%). Amazingly enough, the research shows much of the disparity involves the lack of women in engineering, science and development positions. In the next few years, the STEM fields will become increasingly important as we move toward one of the most technological evolutions in history.
4 Basic Reasons Why We Need More Women In STEM
1) Social Impact
Understanding why women choose certain careers is a subject long studied. We know that having a positive social impact is a strong motivator for why women adopt a certain career. Despite the stigma that disconnects the STEM fields from social impact, it is no accident that most inventions are created by men in the engineering and science fields.
The reason is because these professions learn to design and create solutions out of real world dilemmas. The STEM fields do have great social impact and they tend to solve problems we face in day to day life. More women in the STEM fields would see to it that we had greater social impact in a world where the hardest thing to do is empathize.
2) Diverse Spin on New Inventions
In my past design projects, I have often had to work with large groups of young men and I was the only lady. I enjoyed it and learned a lot about how similarly we all interact with each other! However, I did realize that we thought very different when it came to new ideas. Almost opposite at times.
Through history, our differences have been painted as a negative but I dare to argue that our differences are imperative to the betterment of mankind! Women are phenomenal creatures who have phenomenal perspectives and if we all work together, perhaps we will find solutions we never thought possible. Women could bring in diverse ideas that might have never even been contemplated before.
3) Future Jobs!
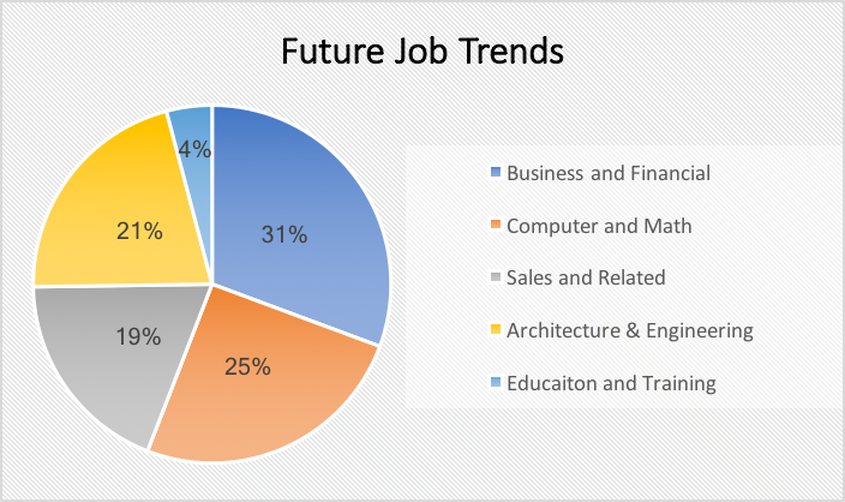
As the climate shifts and we change, the human experience is becoming more and more digital with less reliance on traditional practices such as postal delivery services or “snail mail”. With these changes, we see a drift toward information technology and that is where most of the jobs of the future will come from. I would love it if women could be at the fore-front of running the future managerial job market! Below is a chart highlighting the jobs of the future (it does not include medical fields because that is a whole other chart)
Add up some numbers and the chart above shows that 46% of the jobs will be in STEM related fields which is a large percent of employment opportunities. And with the exception of financial mangers and Wall Street moguls, the jobs left are mostly stuck in sales which generally do not pay as much.
4) School Of Thought
Engineering is often painted as a profession routed only in numbers but that is hardly the case! I would say the main job an engineer has is using numbers and science to solve any given problem! It is where innovation lives! Now those problems are often connected to machinery and infrastructure but the problem you could be facing could be anything from uncomfortable heels to renovating a flooded basement. Whatever the problem, it takes a certain level of creativity to suggest a solution. I think increasing more women in STEM will introduce a level of creativity that we may have never envisioned. It will also help women in terms of understanding risk and thinking critically.
Have you noticed an increase in women in your fields? And how do you think it affects your work environment? I love having discussions so please Comment, Like & Share!
Written By: Jennifer Ladipo